In recent years, 3D printing technology has been revolutionizing many industries with its ability to turn digital designs into three-dimensional objects. The mold manufacturing sector has seen significant transformations thanks to 3D printing, offering flexibility and cost efficiency. We take a look at the essence of 3D printing, its transformative impact on the industry, and how it stacks up against conventional mold manufacturing methods.

What is 3D Printing?
3D printing, or additive manufacturing, is a process that creates physical objects from a digital design by layering materials. Unlike conventional manufacturing methods, 3D printing adds material layer by layer, which can reduce waste and allow for more complex geometries. It uses various materials, including plastics, resins, and metals, making it versatile across a multitude of different applications.
Growth of 3D Printing
The 3D printing industry has witnessed substantial growth over the past decade, both in terms of technological advancements and market expansion. Adoption rates have increased across various sectors including automotive, aerospace, marine, consumer products, and healthcare. Driven by an increased demand for customized products and a need for prototyping, 3D printing is not only reshaping large-scale manufacturing processes but also empowering small businesses and new industries.
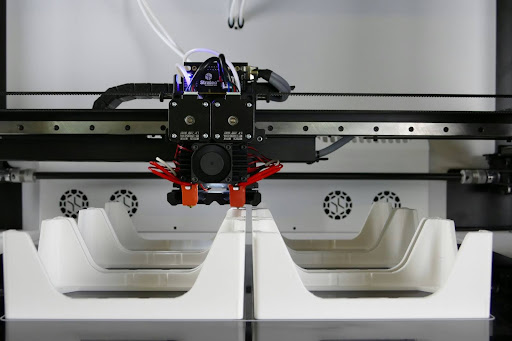
Transforming the Mold Manufacturing Industry
3D printing can bring numerous advantages to the mold manufacturing industry:
- It can reduce the time and cost associated with producing molds, especially for complex and intricate designs that would be challenging to achieve through conventional methods.
- It allows for rapid prototyping, speeding up the design process and enabling faster iterations and refinements.
- It is ideal for low-volume production runs due to its comparative cost-efficiency.
However, 3D printing still faces some challenges:
- 3D printing is not without environmental impacts. The energy consumption of 3D printers and the use of non-recyclable plastics and resins are concerns that the industry continues to address.
- The 3D printing process generally has broader tolerances than conventional methods, which is not ideal for precision components. Manufacture may need to be combined with CNC machining and other post-processing techniques for use in high-tolerance industries such as aerospace and defence.
- Although advancements have broadened the range of materials used in 3D printing, the selection remains limited compared to conventional manufacturing methods. This restricts the use of 3D printing in various industries where materials such as advanced alloys or specialty composites are required.
- 3D printing is not ideal for large production runs primarily because it is generally slower and more costly per unit than traditional mass production methods.
- Whilst the 3D printing industry is growing, there is still a limited number of suppliers who are equipped to handle specific, high-quality 3D printing demands. This scarcity can delay project timelines. Businesses should be asking how close the technology is to be economically usable at scale.
The Plyable Advantage
In order for businesses to take advantage of the reduced lead times possible with 3D printing, the industry needs to expand its supplier base and improve its global distribution capabilities to meet demand more efficiently. This is where Plyable stands out as the optimal solution. Plyable offers rapid, efficient, and cost-effective mold manufacturing services, leveraging a network of skilled suppliers to ensure that even the most urgent demands are met swiftly and without compromising quality.
“3D printing of lamination tools is in its infancy. However, in both direct tooling and as master production at Plyable, we see great promise. We have partner suppliers with the 3D printing machines installed, and we are working with them on trials to gain a better understanding of its current and future suitability for our supply of composite tooling.”
Bill Mattholie, Applications Engineer at Plyable
3D printing is undoubtedly transforming mold manufacturing, offering remarkable opportunities for innovation and efficiency. However, businesses must also consider the practical aspects of integrating new technologies into their operations. Plyable provides a compelling alternative, combining the speed and customization of 3D printing with the practicality and efficiency required in today’s fast-paced market.
Interested in learning more about Plyable? Contact us today to see how we can help you achieve manufacturing excellence with both traditional and innovative technologies.